- Home
- Products
- Medical
-
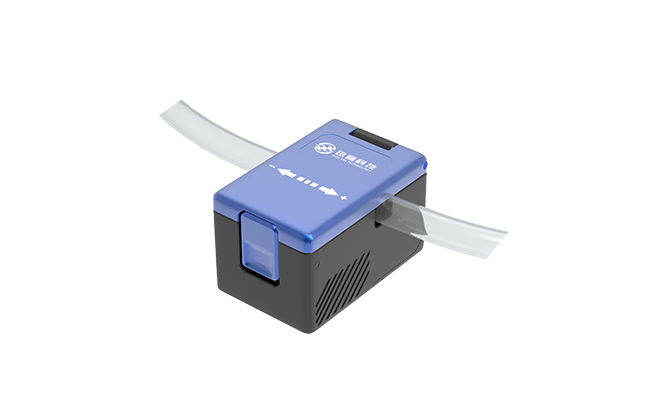

CG Series Clamp-on Ultrasonic Flow Sensors / Flow Meters
CG series ultrasonic clamp-on flow sensors / flow meters are compact in size, and can measure flow a...
-

CM series Clamp-on Ultrasonic Flow Sensor/Flow Meters
The CM series clamp-on ultrasonic flow sensors/flow meters are similar to the CG series flow sensors...
-
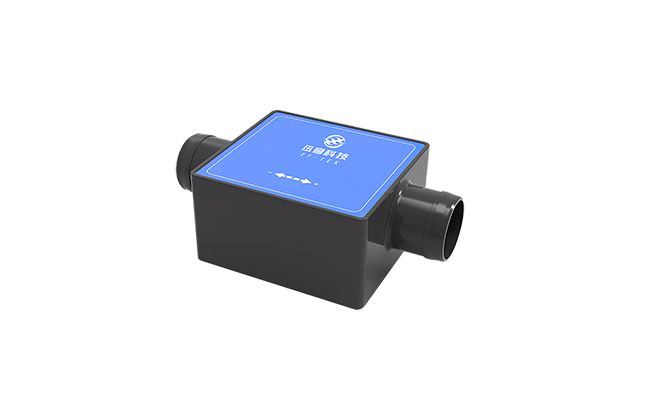

TH series Pulsatile Flow Sensor / Flow Meter
The TH series pulsatile flow rate measurement sensors/flow meters are designed specifically for hear...
-
- Bioprocess
-
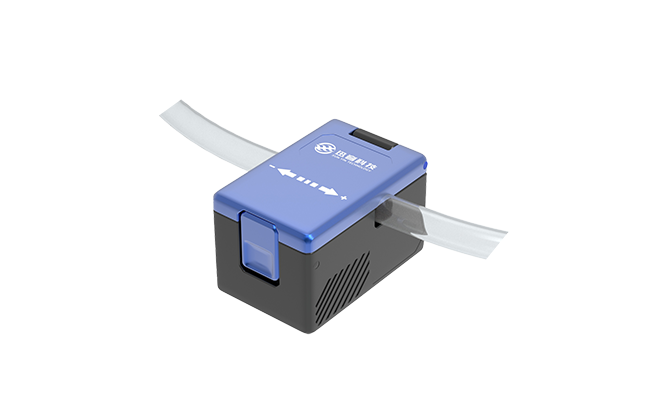

CG series Clamp-on Ultrasonic Flow Sensor / Flow Meter
CG series clamp-on flow sensors / flow meters are compact in size, and can measure flow and output r...
-
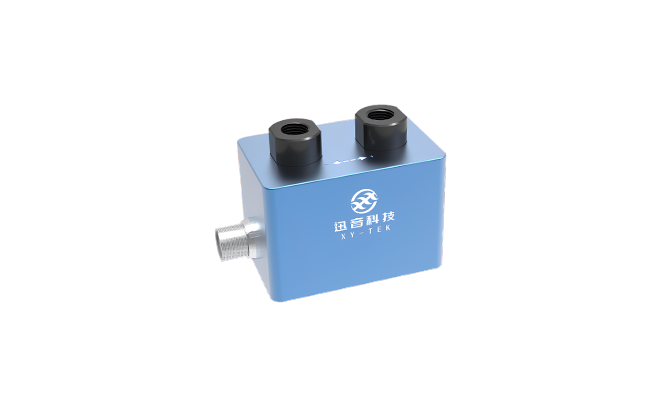

TGU series Low-flow Ultrasonic Flow Sensor / Flow Meter
The TGU Series Low-flow Ultrasonic Flow Sensors / Flow Meters feature a U-shaped measuring channel d...
-
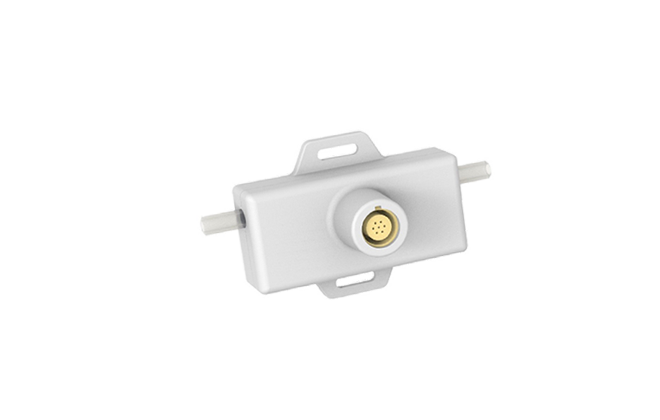
SU series Single-use Ultrasonic Flow Sensor / Flow Meter
The SU single-use ultrasonic flow sensor/flow meter incorporates a disposable measuring channel made...
-
- New Energy
-

CPD series Clamp-on Ultrasonic Flow Sensor / Flow Meter
The CPD series clamp-on ultrasonic flow sensor/flow meters boast a compact design with an integrated...
-

TPD series In-line Ultrasonic Flow Sensor/Flow Meter
The TPD series inline ultrasonic flow sensors/flow meters feature an integrated design with a built-...
-
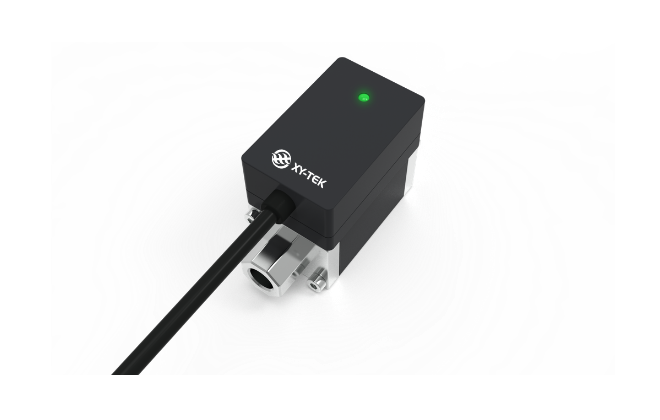

TPK series In-line Ultrasonic Flow Sensor / Flow Meter
The TPK series inline ultrasonic flow sensors/flow meters feature an integrated design with a built-...
-
- Industrial Automation
-

CPD series Clamp-on Ultrasonic Flow Sensor / Flow Meter
The CPD series clamp-on ultrasonic flow sensor / flow meter boasts a compact design with an integrat...
-

TPD series In-line Ultrasonic Flow Sensor/Flow Meter
The TPD series inline ultrasonic flow sensors/flow meters feature an integrated design with a built-...
-

TPK series In-line Ultrasonic Flow Sensor/Flow Meter
The TPK series inline ultrasonic flow sensors/flow meters feature an integrated design with a built-...
-
- Accessories
- Medical
- Applications
- Resources
- News
- Company

















 Pre-Sale
Pre-Sale After-Sale
After-Sale